Umbra has unveiled an overhaul for its rendering middleware for high-end video game development.
The cloud-based features a couple of new upgrades, including the Umbra Cloud. This feature performs geometry processing in the cloud instead of on a local machine, giving developers access to near-unlimited computation and storage capabilities. The Umbra code can use the cloud-generated data as if it were created locally. This makes it possible for smaller teams to take advantage of Umbra’s rendering tech.
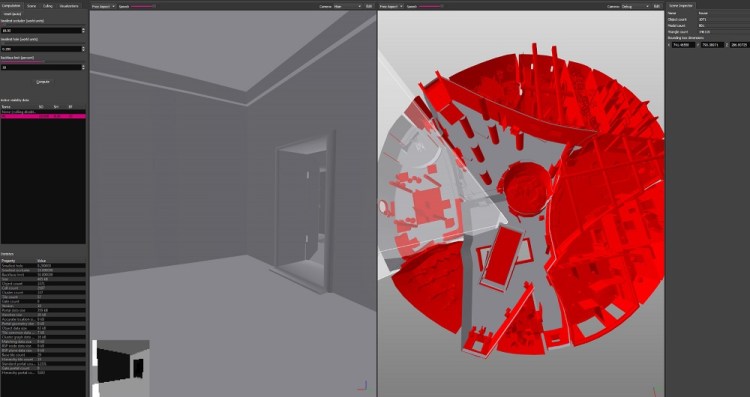
The Helsinki, Finland-based Umbra has already been used in Call of Duty: Advanced Warfare, Destiny, Quantum Break, and The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt. Developers are already using the Umbra Cloud, which is available under a cloud license. Umbra basically handles visibility in 3D worlds, telling the game engine what is visible at any given moment and what is not. That ensures the game worlds run smoothly, even with a lot of graphical detail. And it ensures no computing resources are wasted rendering images that aren’t visible to the player.
“With Umbra Cloud, we have access to a cost-effective and extremely scalable computation infrastructure with zero setup effort,” said Jani Joki, director of engineering at Futuremark and a user of Umbra, in a statement. “It has accelerated our work-flow as we develop our next generation of 3DMark benchmark tests.”
Existing customers get access to the Cloud version of Umbra. The company’s Umbra Debugger is a modern graphical user interface tool for programmers and artists to visualize how Umbra’s visibility system works with their content. The software provides for rapid prototyping and quick debugging, the company said.
“Improved usability and performance are our themes for this year. The addition of cloud computation allows even smaller teams to create large game worlds. The Debugger is a powerful new tool which developers can utilize to use and understand the inner workings of Umbra better” said Otso Mäkinen, the chief technology officer of Umbra.
Umbra creates an optimized database from 3D data, whether it is a small game level or a huge architectural model. Umbra processes the data automatically, which means it can process geometry without any extra work or modifications. Umbra is part of Unity and it is available as a plug-in for Unreal Engine 4.
Umbra was founded in 2006 and it has 12 employees.
“There is a lot of hype surrounding the cloud, but we’ve done extensive work researching it at Umbra and we can really leverage the cloud to make our software far more easily accessible and easier to use,” said Thomas Puha, developer relations manager at Umbra, in an email. “Of course, the other benefit of the cloud is near infinite computation power. This is really just the start for us, there’s a lot of great potential in the cloud for our tech and we already got a few game developers using our cloud tech.”
VentureBeat's mission is to be a digital town square for technical decision-makers to gain knowledge about transformative enterprise technology and transact. Learn More