Want smarter insights in your inbox? Sign up for our weekly newsletters to get only what matters to enterprise AI, data, and security leaders. Subscribe Now
On Wednesday, The Allen Institute for AI (AI2) announced an update to its 7 billion-parameter Open Language Model, OLMo 1.7-7B. The AI now uses a more expansive and diversified Dolma dataset and has an improved education process.
Initially released in February, OLMo is described as a “truly open-source, state-of-the-art large language model.” Its framework includes full pretraining data, training code, model weights, and evaluation.
Dolma 1.5 to 1.7
Today’s update means OLMo 1.7-7B supports longer context length (up from 2,048 to 4,096 tokens) and better performance due to its training procedure and architectural improvements. For the dataset, AI2 has developed Dolma 1.7 which features 2.3 trillion tokens from across its wide range of sources including Dolma CC, Refined Web, StarCoder, C4, Stack Exchange, OpenWebMath, Project Gutenberg, Wikipedia and others.
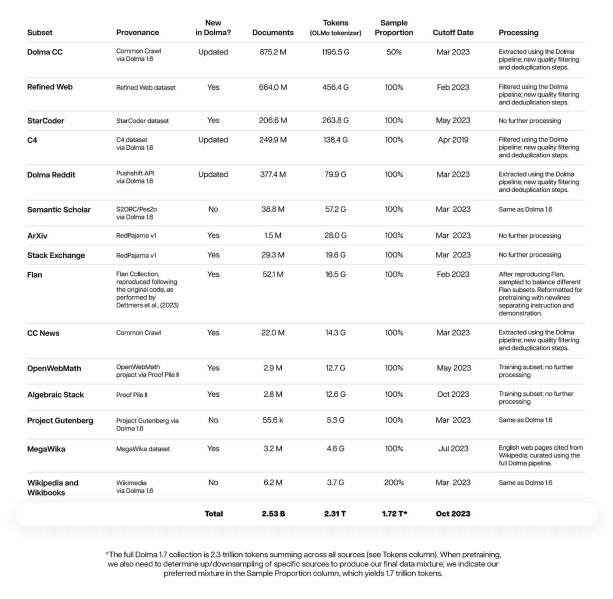
OLMo previously used Dolma 1.5, but that mostly contained web data. In Dolma 1.7, AI2 diversified its mixture of sources, pulling content to handle tasks requiring specialized knowledge, complex reasoning and coding. In addition, the new dataset offers better deduplication, removing whole documents with “a document-level duplication score exceeding a threshold α, which is calculated as the length-normalized average of the paragraph-level duplication scores.”
AI Scaling Hits Its Limits
Power caps, rising token costs, and inference delays are reshaping enterprise AI. Join our exclusive salon to discover how top teams are:
- Turning energy into a strategic advantage
- Architecting efficient inference for real throughput gains
- Unlocking competitive ROI with sustainable AI systems
Secure your spot to stay ahead: https://bit.ly/4mwGngO
Dolma 1.7 also features improved quality filtering. A FastText classifier sorts documents based on high-quality — those well-formatted and covering a wide range of useful domains language models train on — and low-quality text. Examples of the former include Wikipedia, Small Web RSS feeds, and Semantic Scholar. Low-quality subsets include adult entertainment and fake news websites. AI2 says the classifier is trained on approximately 25 GB of data.
Evolved training
Unlike its previous version, OLMo 1.7 uses a two-stage curriculum. In the first stage, researchers train the model from scratch. In the second stage, the data is trained using a curated subset of Dolma 1.7 for another 50 billion tokens “while linearly decaying the learning rate to 0.” AI2 says it curates “this high-quality subset by (1) using all available Wikipedia, OpenWebMath and Flan data, (2) removing Dolma CC, CC News, and Megawika, and (3) rebalancing remaining sources to achieve approximately equal proportions of each.
AI2 claims that thanks to these updates, OLMo 1.7-7B outperforms both Llama 2-7B in MMLU and Llama-2-13B on GSM8K.
The updated OLMo model is licensed with Apache 2.0 while Dolma 1.7 is licensed under ODC-BY. Both are available on Hugging Face today.


